In Apple TV+’s Masters of the Air, the men of the 100th Bombardment Group are known for flying Boeing B-17 planes, also known as Flying Fortresses, which have a real and quite detailed history within the Second World War. Masters of the Air is a war drama following the true story of the 100th Bombardment Group of the U.S. Army Air Forces during World War II, whose unusual death tolls earned them the nickname, the “Bloody Hundredth.” The series is a companion to Tom Hanks and Steven Spielberg’s previous war dramas, Band of Brothers and The Pacific.
While Masters of the Air is very much steeped in real history, from its English setting to Masters of the Air’s characters who are based on real people, another important historical aspect is the actual fighting of the war. Throughout the series, audiences get a glimpse at the true experience of fighting in World War II, and more specifically, of being a part of the Air Forces. Included in this experience is the B-17 bomber plane, which was a staple of the war, and furthermore, is the machine that made up much of the 100th’s lives at that time.

When Masters Of The Air’s Finale Releases & How Many Episodes There Are
Masters of the Air premieres on Apple TV+ on January 26, with several episodes following before the World War II drama miniseries reaches its finale.
Why The B-17 Bomber Was Called The “Flying Fortress”
One of the first things to know about the Boeing B-17 bomber is that its most common nickname was the “Flying Fortress.” The B-17 was first created in the 1930s, specifically for the United States Army Air Corps. Though the prototype crashed during an Air Corps test, the plane outperformed its competitors, and therefore, was brought on as one of the main aircraft used during World War II. Ultimately, the B-17 was called the “Flying Fortress” because of its toughness, prioritizing defenses over bombload, which allowed these planes to often land safely despite heavy damages.
The Flying Fortress earned its name by being speedy, durable, and long-lasting, and from there, the plane quickly became a symbol of American power. Not only was the B-17 significant for the airmen that flew them or the soldiers that watched them from the front lines. The Flying Fortress made an impact on Americans back home, who could only watch the war from afar, and needed reassurance that the United States was performing well. In the end, the B-17 became an icon for both America’s aviation power and their status in the war.
How The B-17 Bomber Was Used In World War 2

As its name suggests, the Boeing B-17 bomber was typically used for bombing by the United States Army Air Forces. The first B-17 planes were used by the Royal Air Force and the U.S.’s 19th Bombardment Group in 1941. Notably, these planes were in use before the attack on Pearl Harbor, and many of them were destroyed during that event. From there, the B-17s traveled around the war effort, from Australia to Java to the Middle East. Eventually, in the summer of 1942, many of the planes were moved to the 100th’s very own Thorpe Abbotts.
In terms of specifics, the Boeing B-17 was most often used for daylight bombing missions against German targets. This meant that, as portrayed in Masters of the Air, airmen would fly their B-17s over German U-boat pens, docks, warehouses, and airfields, and drop bombs on them. These targets were not always in Germany, but ranged from Norway to Africa. Notably, the United States’ daylight bombing was not always successful, and often led to the destruction of B-17s. However, these planes, along with the Royal Air Force, eventually managed to take superiority over German air power.
How Fast B-17 Bombers Can Fly
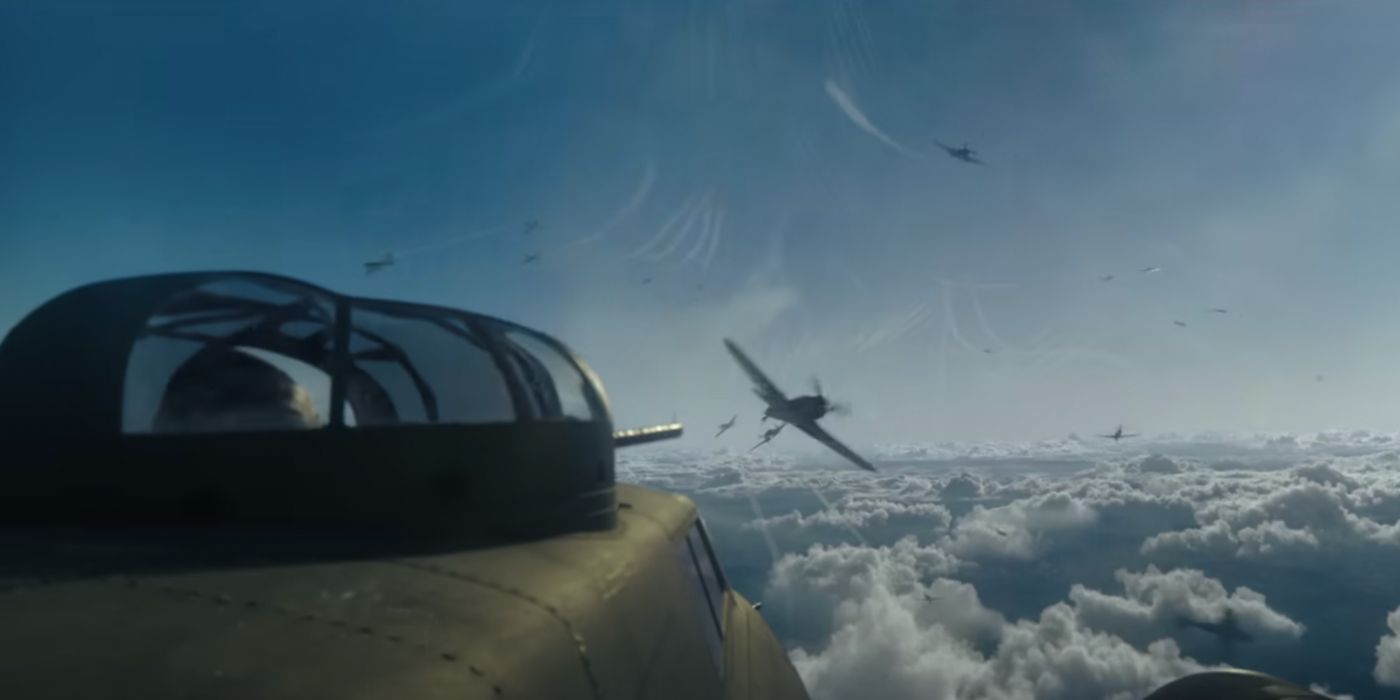

While Flying Fortresses are best-known for their sturdy build, they are also incredibly fast and high-flying planes. When Boeing first introduced the B-17 in 1935, still in its Model 299 stage, its average cruising speed sat at an average of 252 miles per hour. This was much faster than other planes being built at the time, making the B-17 stand out. But in general, any B-17 model has around the same qualities in terms of speed. The B-17 has a maximum speed of 287 miles per hour and a cruising speed of 182 miles per hour.
Over the years, the B-17 had many different models, and at times, this enhanced or decreased its speed. As previously mentioned, one of Boeing’s first B-17 models, Model 299, had a cruising speed of 252 miles per hour. Another B-17 model, the Y1B-17, apparently had a maximum speed of 311 miles per hour. In this way, the B-17 could vary in speed depending on the model being flown, but in the end, it was an aircraft that was typically faster than other military aircraft, which made it particularly special.
When The United States Retired The B-17 Bomber & What Replaced It

Although the B-17 was integral to the Allies during World War II, the planes were quickly phased out by the United States military once the war ended. Once the planes were ferried back across the Atlantic, a great many of them were disassembled and melted down or sold as scrap. However, the B-17 was not entirely extinct. A fraction of the planes used in the war were maintained by the United States and used for other things such as reconnaissance missions and air-sea rescue. B-17s were also used as drones. The B-17 was officially retired from military service in 1959.
The B-17’s quick retirement is less surprising when considering that, by the end of the war, the B-17 was already becoming obsolete. Though the planes were vital in the early years of the war, by 1945 the military had already introduced better aircraft such as the B-24. In fact, according to the Warfare History Network, a B-17 plane never even flew over Japan while hostilities were occurring. In this way, the B-17’s strength and speed could not outlast the war, though they remained prevalent for nearly a decade. The B-17 was replaced by the B-24, then other newer Boeing models.
Are Any B-17 Bombers Still Flying Today?

At this time, there are only four B-17 bombers that could still fly today. In total, there are 45 Flying Fortresses in the world, and 38 of them are located in the United States. For the most part, these B-17s are still in existence, but are being used as historical artifacts rather than true aircraft. Many of them are part of museum displays or are being kept in storage. However, many B-17s are also under restoration, which means they could fly someday in the future. Ultimately, it is shows like Masters of the Air that keep the B-17’s legacy alive.
Masters of the Air
- Release Date
- January 26, 2024
- Cast
- Austin Butler , Callum Turner , Barry Keoghan , Nikolai Kinski , Stephen Campbell Moore , Sawyer Spielberg , Isabel May , Anthony Boyle
- Where To Watch
- Apple TV+